This post outlines how to manage the errors and status codes using modal validation, exception filter s and global exception handling.
The common status codes that you deal while you are writing Web API code
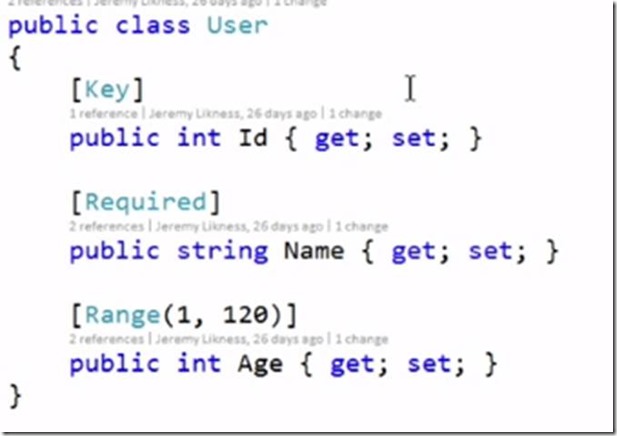
Model Validation is a very power full capability of web API. It is a data annotation library and allows you to annotate your classes and indicate different types, ranges and validations. You can add your own error using ModelState.AddModelError method and then you can check with ModelState.IsValid. The good thing about ModelState is that you can serialize and send it to client.
The sample model looks as follows
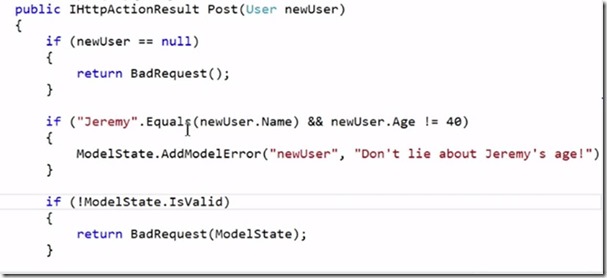
You can write the following validation code in controller, for example post request to create a new user
Once the validation is in place then you can use following built-in helpers to return information and serialize the ModelState
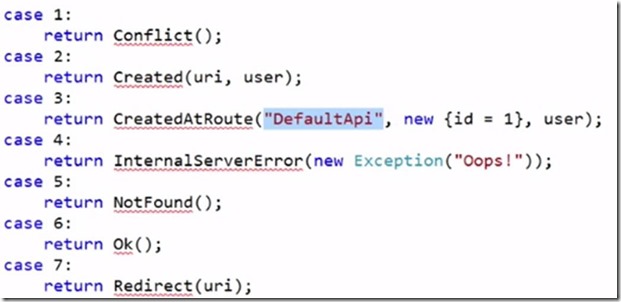
These helpers take the most common cases and send the information back example BadRequest (); other examples using helpers follows
If there isn’t any helper available then you can use StatusCode (HttpStatusCode.Ambiguous);
Conflict is for example if somebody tries to create a user account and it is matched email already in the database then you can use Conflict.
Exception Filters
Exception Filters have few attributes that can be used while designing your API. Exception filters are reusable. You can apply them at action, controller or global level. When you are inside the action method, you do not have much access to it. Exception is still thrown when debugger is on. You can also set the response on filter. Sample custom NotImplementedFilter looks as below
The NotImplemented Filter code as below
![]()
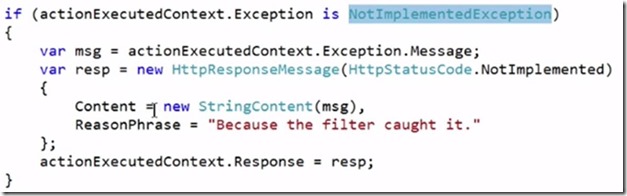
In NotImplementedFilter you have OnException which has context that specific to the action
If this context has notimplemented exception then we are changing the message and returning in the response.
So when you apply the filter on controller level or action level then this will get caught in above piece of code.
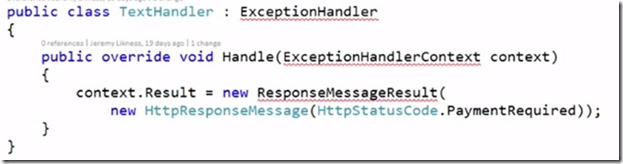
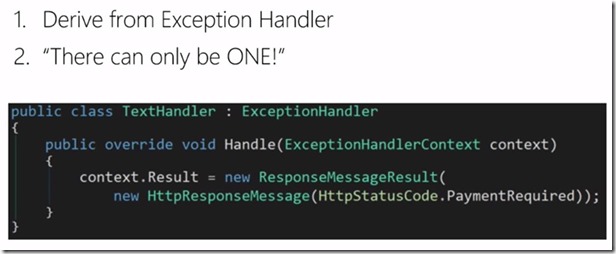
For example, if there is no attribute on controller or action method then this get caught in in sample exception handler
It does have a handle on the exception and returns a message PaymentRequired. You write a custom filter and exception handler return a message based on the filter. It returns a message from handler when there is a no much for exception filter.
Global Exception handling
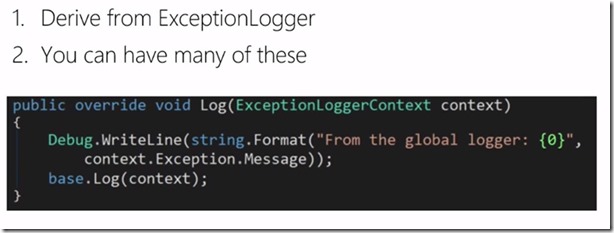
With the filters, there may be certain type of exceptions that you want to do something special then you need a global way instead of doing at each controller or action method level. The tricky areas for errors are
Let us say Web API going through the route and trying to figure out the controller and some reason you get dependency error then it blows up, to deal these you have message handlers that runs in separate pipeline.
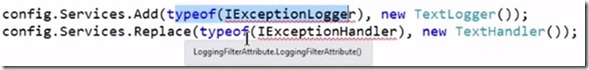
You can apply filter globally and add handlers as below
Filters are contextual and usually to deal with the exceptions within the controller and action level where as global handlers are to handle logging and to catch exceptions that are not possible with filters.